Usage of QR code in ROS
12 Dec 2019
Post Tags
ROS QRcode Camera-model LocalizationTable of Content
- Table of Content
- 1. Pose estimation and camera model
- 2. Ar_track_alvar (A QRcode package in ROS)
- reference
Using vision to do the indoor localization is one of the most feasible and general way currently. Especially in robotics, AR tag, which is a kind of QR code liked marker, is widely used in ROS,Robotic operation system.
1. Pose estimation and camera model
A camera model can be described by intrinsic model and extrinsic model. Intrinsic model includes those inherent features of one camera, like distortion, focal length, and pixel size. Extrinsic model indicate the pose of a camera inside a world frame.
1.1 Intrinsic model
The camera model can characterize transformations from a 3D world frame to a 2D image plane. Here using K to represent the intrinsic matrix1. $[P_x,P_y]$ is a translation vector indicating the offset of 2D points in a image plane. Where $[x_{pix},\ y_{pix}]^T$ represents a point in camera image planes (pixel coordinates), $[X_{c},\ Y_{c},\ Z_{c}]^T$ represents a point in 3D camera coordinates.
\[(1). \left[\begin{array}{c}{x_{p i x}} \\ {y_{p i x}} \\ {1}\end{array}\right]=\textbf{K} \left[\begin{array}{c}{X_{c}} \\ {Y_{c}} \\ {Z_{c}}\end{array}\right],Where\ \textbf{K}=\underbrace{\left[\begin{array}{ccc}{f_{x}} & 0 & {p_{x}} \\ {0} & {f_{y}} & {p_{y}} \\ {0} & {0} & {1} \end{array}\right]}_{intrinsic\ matrix}\]Distortion caused by optical components in the camera is another problem in real world image systems. The distortion of an image can be characterized by using a mapping function $\textbf{D}$, $[x_{distorted},\ y_{distorted}]^T=D([x_{ideal},\ y_{ideal}]^T)$ :
\[(2). \begin{array}{l}{x_{\text {distorted }}=x_{\text {ideal}}\left(1+k_{1}^{\star} r^{2}+k_{2}^{\star} r^{4}+k_{3}^{\star} r^{6}\right)} \\ {y_{\text {distorted }}=y_{\text {ideal}}\left(1+k_{1}^{\star} r^{2}+k_{2}^{\star} r^{4}+k_{3}^{\star} r^{6}\right)}\end{array}\]Where $[x_{distorted},\ y_{distorted}]^T$ represents the point in distorted images, $[x_{ideal},\ y_{ideal}]^T$ means the point in ideal images. $\textbf{r}$ expresses the distance to the image center, $k_1,k_2,k_3$ are distortion factors, which respect to different camera and lens.
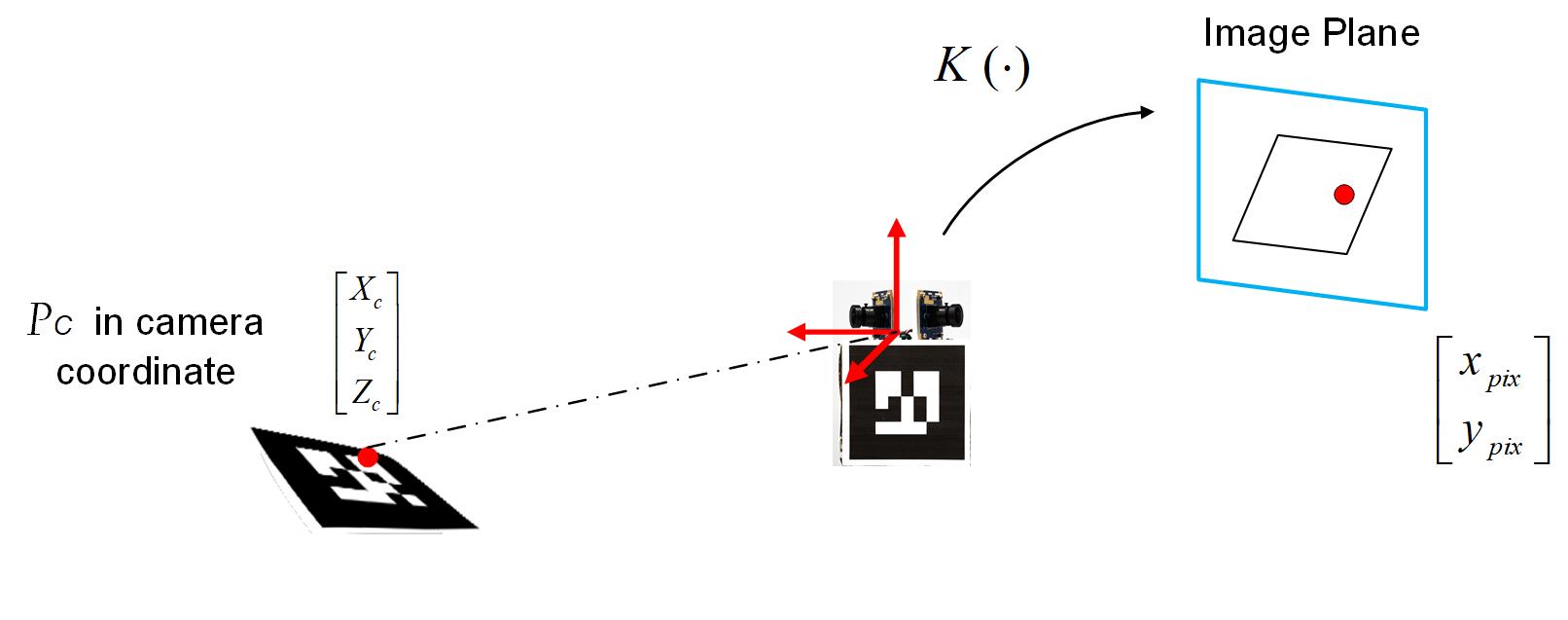 <p>Figure. Camera model transform point from 3D to 2D</p>
<p>Figure. Camera model transform point from 3D to 2D</p>
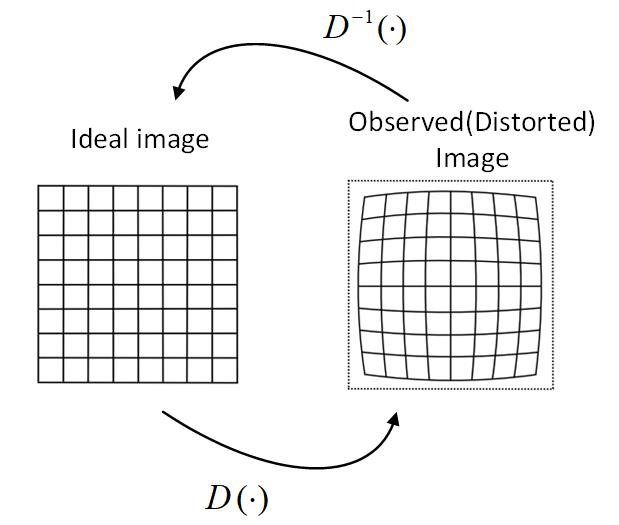
Figure. Distortion transfer
1.2 Extrinsic model(Pose estimation)
Extrinsic parameters indicate the pose of cameras related to the world frames, which is represented by the rotation matrix $\mathbf{R}$ and translation vector $\mathbf{t}$. The transformation from world frames $\mathbf{P_{w}}$ to camera coordinates $\mathbf{P_{c}}$ is showing below, in equation (3).
\[(3). \mathbf{P_{c}} = [\mathbf{R} | \mathbf{t}] \mathbf{P_{w}}\]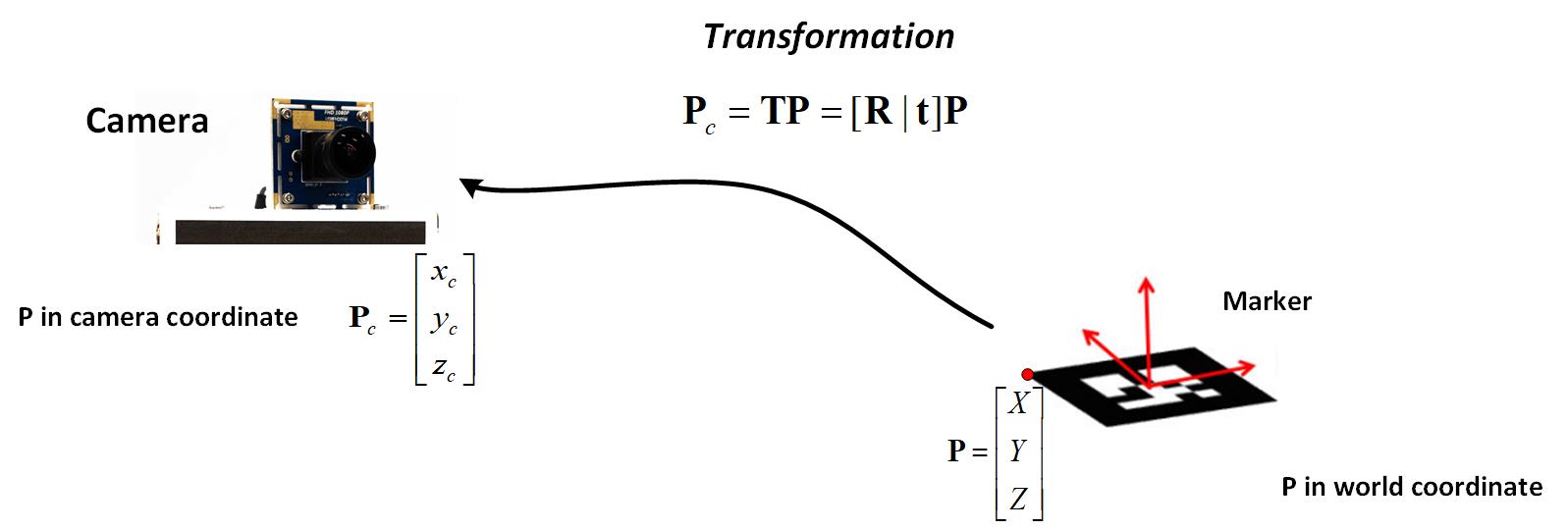 <p>Figure. The transformation from world frame to camera coordinate</p>
<p>Figure. The transformation from world frame to camera coordinate</p>
Combining the equation(1), (2), and (3), the transformation from world coordinates to image planes can be established in equation (4).
\[(4). { \left[ \begin{array}{c} {x_{pix}}\\y_{pix}\\{1}\end{array}\right ]}{ =\textbf{D}( { \textbf{K}\left[ \begin{array}{c} x_c\\ y_c\\ z_c \end{array} \right ]} )} { =\underbrace{ \textbf{D}( \underbrace{\textbf{K}\underbrace{[\textbf{R}|\textbf{t}] { \left[ \begin{array}{c} X_w\\Y_w\\Z_w\\1\end{array}\right ]} )}_{world\ coords\ to\ camera\ coords}}_{camera\ coords\ to\ film\ coords}}_{film\ coords\ to\ pixel\ coords}}\]In (4), the intrinsic parameters, $\textbf{D}$, and $\textbf{K}$ can be identified by doing camera calibration and the $\mathbf{P_w}$ can be known by using prior designed artificial features. Finally, $\textbf{R}$ and $\textbf{t}$ can be retrieved By solving (4).
2. Ar_track_alvar (A QRcode package in ROS)
2.1 Introduction of Ar_track_alvar
Ar_track_alvar is a package in ROS based on ALVAR library. ALVAR is a suite of SDKs and products that help researchers and engineers to create augmented reality applications. In Ar_track_alvar, it provides the fast object recognition and tracking through fiducials. The fiducials or markers can be also generated with Ar_track_alvar, which looks like QR-code. The markers with several features help to be detected, such as clear border and unique pattern. Combined with the prior knowledge, the size of markers and camera intrinsic matrix, the 2D image plane will be transformed to 3D world frame. Here is the official website of Ar_track_alvar.
2.2 Launch File
<launch>
<node name="usb_cam" pkg="usb_cam" type="usb_cam_node" output="screen" >
<param name="video_device" value="/dev/video1" />
<param name="image_width" value="1280"/>
<param name="image_height" value="720"/>
<param name="pixel_format" value="yuyv" />
<param name="camera_frame_id" value="usb_cam" />
<param name="io_method" value="mmap"/>
<param name="camera_info_url" type="string" value="file://$(find robot_vision)/launch/calib170/white.yaml" />
</node>
<node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="world_to_cam"
args="0 0 0.5 1.04 0 -1.57 /map usb_cam 10" />
<arg name="marker_size" default="4.5" />
<arg name="max_new_marker_error" default="0.08" />
<arg name="max_track_error" default="0.2" />
<arg name="cam_image_topic" default="/usb_cam/image_raw" />
<arg name="cam_info_topic" default="/usb_cam/camera_info" />
<arg name="output_frame" default="usb_cam" />
<node name="ar_track_alvar" pkg="ar_track_alvar" type="individualMarkersNoKinect" respawn="false" output="screen">
<param name="marker_size" type="double" value="$(arg marker_size)" />
<param name="max_new_marker_error" type="double" value="$(arg max_new_marker_error)" />
<param name="max_track_error" type="double" value="$(arg max_track_error)" />
<param name="output_frame" type="string" value="$(arg output_frame)" />
<remap from="camera_image" to="$(arg cam_image_topic)" />
<remap from="camera_info" to="$(arg cam_info_topic)" />
</node>
</launch>
2.3 Predefined Ar_track_alvar Message header
The information shared between ROS nodes, processes, is packaged in ‘messages’. A predefined Ar_track_alvar message is shown:
AlvarMarkers message:
One AlvarMarkers message may includes several ‘AlvarMarker’ message, the number of ‘AlvarMarker’ message depends on how many marks are found by camera.

AlvarMarker message:
AlvarMarker message contains the 6 degrees of freedom pose information.

2.4 Example code in C++
When writing the application to solve the position and id_number of Alvar marker in C++, one thing should be alert:
When you have multiple markers at same time alvarmarkers message will wrapper all alvarmark inside a array structure, which like: message.markers[i].
Here is an example about how to use alvarmarkers message in a callback function:
void AR::pose_CB(const ar_track_alvar_msgs::AlvarMarkers &msg) {
if (!msg.markers.empty()) {
int mkr_cnt = msg.markers.size();
for(i=0;i<mkr_cnt;i++){
print("maker_id = %d", msg.markers[i].id);
tf::Quaternion q(msg.markers[i].pose.pose.orientation.x, msg.markers[i].pose.pose.orientation.y, msg.markers[i].pose.pose.orientation.z, msg.markers[i].pose.pose.orientation.w);
tf::Matrix3x3 m(q);
double roll, pitch, yaw;
m.getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
// return the pose of robot1
printf("the position of marker%d x= %f,y=%f with pitch=%f \n",msg.markers[i].id,msg.markers[i].pose.pose.position.x,msg.markers[i].pose.pose.position.z, pitch);
}
}
}